Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nagai, Takayuki; Hasegawa, Takehiko*
JAEA-Research 2023-008, 41 Pages, 2023/12
To reduce the risks posed by stored the high-level radioactive liquid waste (HAW), Tokai Vitrification Facility (TVF) is working to produce the HAW into vitrified bodies. With the aim of steady vitrification of HAW in TVF, the vitrification technology section has manufactured a new 3rd melter with an improved bottom structure and is working to verify the performance of this melter. In this study, solidified glass samples were taken from simulated vitrified bodies produced by flowing molten glass during the bottom drain-out test in the operation confirmation of the TVF 3rd melter. And the properties of the surface layer and fracture surface of the vitrified bodies were evaluated by using Raman spectroscopy, synchrotron radiation XAFS measurement, and laser ablation inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy (LA ICP-AES) analysis. As a result of measuring the surface layer and fracture surface of the solidified samples produced on an actual scale, a slight difference was confirmed between the properties of the surface layer and those of the fracture surface. Since the chemical composition of these simulated vitrified bodies does not contain platinum group elements, it is expected that the glass structure of solidified glass samples is different from that of the actual vitrified body. However, this sample measuring was a valuable opportunity to evaluate samples produced by using the direct energized joule heating method. The properties of cullet used the operation confirmation of the TVF 3rd melter and the cullet of another production lot were measured and analyzed in the same manner under the measuring conditions of solidified glass samples. As a result, it was confirmed that cullet with different producing histories have different glass structures even with the same chemical composition, and that differences in glass structures remain in the glass samples after melting these cullet.
Miyabe, Masabumi; Kato, Masaaki*; Hasegawa, Shuichi*
Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 38(2), p.347 - 358, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.02(Chemistry, Analytical)To develop remote isotopic analysis for the nuclids with small isotope shifts, Doppler-free fluorescence spectroscopy of Ca was performed using laser ablation plume. Counter-propagating laser beams from two external cavity diode lasers were used to irradiate the plume in order to excite the ground-state Ca atoms to the  D
D state through a double resonance scheme of
state through a double resonance scheme of  S
S

 P
P

 D
D . Subsequently, we measured fluorescence spectra associated with the relaxation from the
. Subsequently, we measured fluorescence spectra associated with the relaxation from the  D
D to
to  P
P states. The linewidth measured at 1 ms delay after ablation under helium gas pressure of 70 Pa was found to be less than 70 MHz, which was about 1/30 of the linewidth of the Doppler-limited fluorescence spectrum. A broad Gaussian pedestal was observed at less than 600 micro-second delay in the temporal variation in fluorescence spectra, and it was most likely due to the velocity-changing collision. Additionally, the pressure broadening rate coefficient for the second-step
states. The linewidth measured at 1 ms delay after ablation under helium gas pressure of 70 Pa was found to be less than 70 MHz, which was about 1/30 of the linewidth of the Doppler-limited fluorescence spectrum. A broad Gaussian pedestal was observed at less than 600 micro-second delay in the temporal variation in fluorescence spectra, and it was most likely due to the velocity-changing collision. Additionally, the pressure broadening rate coefficient for the second-step  P
P

 D
D transition was determined to be 46.0 MHz/torr from the spectra measured under various gas pressures. We evaluated analytical performances such as linearity of the calibration curve, limit of detection, and measurement accuracy using fluorescence signals of three naturally occurring Ca isotopes (i.e.,
transition was determined to be 46.0 MHz/torr from the spectra measured under various gas pressures. We evaluated analytical performances such as linearity of the calibration curve, limit of detection, and measurement accuracy using fluorescence signals of three naturally occurring Ca isotopes (i.e.,  Ca,
Ca, 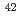 Ca, and
Ca, and 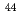 Ca). The limit of detection of isotopic abundance was estimated to be 0.09% from the 3-sigma criteria of the background. These results suggest that this spectroscopic technique is promising for remote isotopic analysis of nuclides with small isotope shifts.
Ca). The limit of detection of isotopic abundance was estimated to be 0.09% from the 3-sigma criteria of the background. These results suggest that this spectroscopic technique is promising for remote isotopic analysis of nuclides with small isotope shifts.
Miyabe, Masabumi; Oba, Masaki; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Kato, Masaaki*; Hasegawa, Shuichi*; Wakaida, Ikuo
Applied Physics A, 126(3), p.213_1 - 213_10, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:38.16(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The dynamic behavior of an ablation plume in low pressure rare gas ambient was investigated with laser-induced fluorescence imaging spectroscopy for three refractory metals, i.e. titanium, zirconium and hafnium. A comparison of the plume expansion behaviors for the species of these elements revealed an atomic weight effect on the plume structure formation. A hemispherical thin layer and cavity structure reported previously for gadolinium were observed also for these elements. It was found that the plume size increases as well as the layer thickness decreases with increasing atomic weight. For ground state atoms of Ti, substantial amount of atoms were observed even at the center of the plume. Also, the persistence of the Ti atomic plume was as long as 300  s, which was significantly longer than the other species studied. Furthermore, the mass-dependent elemental separation was observed in the ablation plume produced from a multielement sample. These results suggest that the observed plume structure arises from the ion-electron recombination process and the recoil of the ablated species during the multiple collisions with gas atoms.
s, which was significantly longer than the other species studied. Furthermore, the mass-dependent elemental separation was observed in the ablation plume produced from a multielement sample. These results suggest that the observed plume structure arises from the ion-electron recombination process and the recoil of the ablated species during the multiple collisions with gas atoms.
Nagai, Takayuki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Inose, Takehiko*; Sato, Seiichi*; Hatakeyama, Kiyoshi*; Hirono, Kazuya*; Homma, Masanobu*; Kobayashi, Hiromi*; Takahashi, Tomoe*; et al.
JAEA-Research 2018-007, 87 Pages, 2018/11
To select the chemical composition of a glass frit which can increase the waste content, the simulated waste glass samples prepared from a borosilicate glass frit including vanadium (V) were investigated by using Laser Ablation (LA) ICP-AES analysis, Raman spectrometry, and synchrotron XAFS measurement in this study on foundation business of the Agency for Natural Resources and Energy.
Miyabe, Masabumi; Oba, Masaki; Jung, K.; Iimura, Hideki; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Kato, Masaaki; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Khumaeni, A.*; Wakaida, Ikuo
Spectrochimica Acta, Part B, 134, p.42 - 51, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:91.3(Spectroscopy)Spectroscopic properties of atomic species of plutonium were investigated by combining laser ablation and resonance absorption techniques for the analysis of a plutonium oxide sample. For 17 transitions of Pu atoms and ions, the absorbance, isotope shift, and hyperfine splitting were determined via Voigt profile fitting of the recorded absorption spectra. Three transitions were selected as candidates for analytical use. Using these transitions, we investigated the analytical performance that was attainable and determined a correlation coefficient R2 between the absorbance and plutonium concentration of 0.9999, a limit of detection of 30-130 ppm, and a relative standard deviation of approximately 6% for an abundance of  Pu of 2.4%. These results demonstrate that laser ablation absorption spectroscopy is applicable to the remote isotopic analysis of highly radioactive nuclear fuels and waste materials containing multiple actinide elements.
Pu of 2.4%. These results demonstrate that laser ablation absorption spectroscopy is applicable to the remote isotopic analysis of highly radioactive nuclear fuels and waste materials containing multiple actinide elements.
Kumada, Takayuki; Otobe, Tomohito; Nishikino, Masaharu; Hasegawa, Noboru; Hayashi, Terutake*
Applied Physics Letters, 108(1), p.011102_1 - 011102_4, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:49.56(Physics, Applied)The dynamics of photomechanical spallation during femtosecond laser ablation of fused silica was studied by time-resolved reflectivity with double pump pulses. Oscillation of reflectivity was caused by interference between the probe pulses reflected at the sample surface and the spallation layer, and was enhanced when the surface is irradiated with the second pump pulse within a time interval of several picoseconds after the first pump pulse. However, as the time-interval was increased, the oscillation amplitude decreased with an exponential decay time of 10 ps. The oscillation disappeared when the interval exceeded 20 ps. This result suggests that the formation time of the spallation layer is approximately 10 ps.
Nishikino, Masaharu; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Hasegawa, Noboru; Ishino, Masahiko; Minami, Yasuo*; Suemoto, Toru*; Onishi, Naofumi*; Ito, Atsushi*; Sato, Katsutoshi*; Faenov, A.*; et al.
X-Ray Lasers and Coherent X-Ray Sources; Development and Applications XI (Proceedings of SPIE, Vol.9589), p.958902_1 - 958902_7, 2015/09
Hasegawa, Noboru; Nishikino, Masaharu; Tomita, Takuro*; Onishi, Naofumi*; Ito, Atsushi*; Eyama, Tsuyoshi*; Kakimoto, Naoya*; Izutsu, Rui*; Minami, Yasuo*; Baba, Motoyoshi*; et al.
X-Ray Lasers and Coherent X-Ray Sources; Development and Applications XI (Proceedings of SPIE, Vol.9589), p.95890A_1 - 95890A_8, 2015/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:55.4(Optics)We have improved a soft X-ray laser (SXRL) interferometer synchronized with a Ti:Sapphire laser pulse to observe the single-shot imaging of the nano-scaled structure dynamics of the laser induced materials. By the precise imaging optics and double time fiducial system having been installed, the lateral resolution on the sample surface and the precision of the temporal synchronization between the SXRL and Ti:Sapphire laser pulses were improved to be 700 nm and 2 ps, respectively. By using this system, the initial stage (before 200 ps) of the ablation process of the Pt surface pumped by 80 fs Ti:Sapphire laser pulse was observed by the comparison between the soft X-ray reflective image and interferogram. We have succeeded in the direct observation of the unique ablation process around the ablation threshold such as the rapid increase of the surface roughness and surface vibration.
Miyabe, Masabumi; Oba, Masaki; Iimura, Hideki; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Khumaeni, A.*; Kato, Masaaki; Wakaida, Ikuo
Spectrochimica Acta, Part B, 110, p.101 - 117, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:81.83(Spectroscopy)The dynamic behavior of an ablation plume in ambient gas has been investigated by laser-induced fluorescence imaging spectroscopy. The second harmonic beam from an Nd:YAG laser (0.5-6J/cm ) was focused on a sintered oxide pellet or a metal chip of gadolinium. The produced plume was subsequently intersected with a sheet-shaped UV beam from a dye laser so that time-resolved fluorescence images were acquired with an intensified CCD camera at various delay times. The obtained cross-sectional images of the plume indicate that the ablated ground state atoms and ions of gadolinium accumulate in a hemispherical contact layer between the plume and the ambient gas, and a cavity containing a smaller density of ablated species is formed near the center of the plume. At earlier expansion stage, another luminous component also expands in the cavity so that it coalesces into the hemispherical layer. The splitting and coalescence for atomic plume occur later than those for ionic plume. Furthermore, the hemispherical layer of neutral atoms appears later than that of ions; however, the locations of the layers are nearly identical. This coincidence of the appearance locations of the layers strongly suggests that the neutral atoms in the hemispherical layer are produced as a consequence of three-body recombination of ions through collisions with gas atoms. The obtained knowledge regarding plume expansion dynamics and detailed plume structure is useful for optimizing the experimental conditions for ablation-based spectroscopic analysis.
) was focused on a sintered oxide pellet or a metal chip of gadolinium. The produced plume was subsequently intersected with a sheet-shaped UV beam from a dye laser so that time-resolved fluorescence images were acquired with an intensified CCD camera at various delay times. The obtained cross-sectional images of the plume indicate that the ablated ground state atoms and ions of gadolinium accumulate in a hemispherical contact layer between the plume and the ambient gas, and a cavity containing a smaller density of ablated species is formed near the center of the plume. At earlier expansion stage, another luminous component also expands in the cavity so that it coalesces into the hemispherical layer. The splitting and coalescence for atomic plume occur later than those for ionic plume. Furthermore, the hemispherical layer of neutral atoms appears later than that of ions; however, the locations of the layers are nearly identical. This coincidence of the appearance locations of the layers strongly suggests that the neutral atoms in the hemispherical layer are produced as a consequence of three-body recombination of ions through collisions with gas atoms. The obtained knowledge regarding plume expansion dynamics and detailed plume structure is useful for optimizing the experimental conditions for ablation-based spectroscopic analysis.
Nishikino, Masaharu; Hasegawa, Noboru; Ishino, Masahiko; Ochi, Yoshihiro; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Yamagiwa, Mitsuru; Kato, Yoshiaki*
Chinese Optics Letters, 13(7), p.070002_1 - 070002_3, 2015/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.97(Optics)Hasegawa, Noboru; Tomita, Takuro*; Nishikino, Masaharu; Eyama, Tsuyoshi*; Kakimoto, Naoya*; Minami, Yasuo*; Baba, Motoyoshi*; Onishi, Naofumi*; Ito, Atsushi*; Kawachi, Tetsuya; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2015-001, p.17 - 20, 2015/07
We have succeeded in simultaneous observation of the ablation front and the expansion front with thin filmy structure in the femto-second laser ablation process of a gold target by using the 13.9 nm soft X-ray probe (incident angle to the sample  70 deg) with soft X-ray interferometer. The dependence on the laser local fluence and materials was obtained by the comparison between gold and tungsten.
70 deg) with soft X-ray interferometer. The dependence on the laser local fluence and materials was obtained by the comparison between gold and tungsten.
Kumada, Takayuki; Akagi, Hiroshi; Itakura, Ryuji; Otobe, Tomohito; Nishikino, Masaharu; Yokoyama, Atsushi
Applied Physics Letters, 106(22), p.221605_1 - 221605_5, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:13.81(Physics, Applied)The dynamics of femtosecond laser ablation of transparent polymers were examined using time-resolved reflectivity. When these polymers were irradiated by a pump pulse with fluence above the ablation threshold of 0.8-2.0 J/cm , we observed the oscillation of the reflectivity caused by the interference between the reflected probe pulses from the sample surface and the thin layer due to the non-thermal photomechanical effects of spallation. As the fluence of the pump pulse increased, the separation velocity of the thin layer increased from 6 km/s to an asymptotic value of 11 km/s. It is suggested that the velocities are determined by shock-wave velocities of the photo-excited layer.
, we observed the oscillation of the reflectivity caused by the interference between the reflected probe pulses from the sample surface and the thin layer due to the non-thermal photomechanical effects of spallation. As the fluence of the pump pulse increased, the separation velocity of the thin layer increased from 6 km/s to an asymptotic value of 11 km/s. It is suggested that the velocities are determined by shock-wave velocities of the photo-excited layer.
Nishikino, Masaharu; Hasegawa, Noboru; Tomita, Takuro*; Eyama, Tsuyoshi*; Kakimoto, Naoya*; Onishi, Naofumi*; Ito, Atsushi*; Baba, Motoyoshi*; Minami, Yasuo*; Kawachi, Tetsuya; et al.
Reza Gakkai Dai-471-Kai Kenkyukai Hokoku; Tanhacho Ryoshi Bimu Hassei To Sono Oyo, p.9 - 12, 2014/12
no abstracts in English
Inogamov, N. A.*; Zhakhovsky, V. V.*; Ashitkov, S. I.*; Emirov, Y. N.*; Faenov, A. Y.*; Pikuz, T. A.*; Ishino, Masahiko; Kando, Masaki; Hasegawa, Noboru; Nishikino, Masaharu; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 500(11), p.112070_1 - 112070_6, 2014/05
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:98.65(Physics, Applied)The mechanism of formation and geometry of surface structures are discussed for the case of single pulse acting on a well-polished metal surface. We demonstrate that the complex surface nano-structures are formed after laser irradiation due to the thermomechanical spallation of ultrathin surface layer of melt. Spallation is accompanied by a strong foaming of melt followed by breaking of the foam. After several nanoseconds the foam remnants freeze up with formation of complex nano-structures on a target surface.
Saeki, Morihisa; Oba, Hironori; Yokoyama, Atsushi
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 59, p.732 - 735, 2007/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Optics)We have performed laser ablation of silicon in neon gas and benzene vapor. The reaction mechanism of the ablated silicon atoms with the neon atoms and benzene molecules were investigated by space- and time-resolved emission spectroscopy. The ablation in the neon gas suggested that (1) the neutral neon atoms are excited to 2pn states lying in 18-19 eV and (2) the neutral neon atoms are excited by electronic-to-electronic and translational-to-electronic energy transfer from the silicon ions. In the ablation in the benzene vapor, we found that the benzene molecules are decomposed into C2 and CH radicals by the collision with the silicon atoms.
Wang, H.*; Oba, Hironori; Saeki, Morihisa; Miyabe, Masabumi; Shibata, Takemasa; Miyatake, Hiroari*; Iimura, Hideki
Applied Physics B, 81(8), p.1127 - 1133, 2005/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:31.16(Optics)Laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy has been employed to characterize the plume produced in nanosecond laser ablation of metallic neodymium. The kinetic-energy distributions of the neutral and ionized atoms in the plume under both vacuum and gas environments have been investigated. The population distribution of metastable levels in the ablated atoms was also derived. The results show some metastable states are more heavily populated than predicted by a Boltzman-type distribution. These investigations provide preliminary data for the design of a new type of resonance photo-ionization laser ion source as well as for hign-resolution laser spectroscopy of refractory elements.
Saeki, Morihisa; Hirata, Koichi*; Sakka, Tetsuo*; Oba, Hironori; Yokoyama, Atsushi
Journal of Applied Physics, 98(4), p.044912_1 - 044912_6, 2005/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:13.67(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Wang, H.*; Miyatake, Hiroari*; Oba, Hironori; Saeki, Morihisa; Miyabe, Masabumi; Shibata, Takemasa; Iimura, Hideki
Review of Scientific Instruments, 75(10), p.3775 - 3776, 2004/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.27(Instruments & Instrumentation)Laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy has been employed to characterize a plume produced in nanosecond laser ablation of metallic neodymium. Kinetic energy distributions of ions and neutrals in the plume were investigated as functions of processing parameters such as laser fluence and ambient gas pressure. Population distributions of metastable levels in the ablated atoms were also measured. These investigations provide useful data for the design of a new types of resonance photo-ionization ion source and also for high-resolution laser spectroscopy.
 optical spectroscopy of ablation plume for preparations of nanostructured TiO
optical spectroscopy of ablation plume for preparations of nanostructured TiO thin films by pulsed laser deposition
thin films by pulsed laser depositionKitazawa, Shinichi
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Part 1, 43(9A), p.6335 - 6341, 2004/09
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:54.92(Physics, Applied)Nanostructured TiO thin films on
thin films on  -Al
-Al O
O (0001) substrates prepared by pulsed laser deposition (PLD) were analyzed and evaluated in terms of the buffer O
(0001) substrates prepared by pulsed laser deposition (PLD) were analyzed and evaluated in terms of the buffer O gas pressure (0 - 80 Pa) dependencies by optical spectroscopy and surface morphology. Optical emission spectra of the ablation plume from Ti and TiO
gas pressure (0 - 80 Pa) dependencies by optical spectroscopy and surface morphology. Optical emission spectra of the ablation plume from Ti and TiO targets were measured in-situ. The contribution from TiO molecules was observed by narrow-band photometry. The surface morphology was observed by an atomic force microscope (AFM), revealing the pressure dependence of nanostructures. The crystallographic structures of prepared TiO
targets were measured in-situ. The contribution from TiO molecules was observed by narrow-band photometry. The surface morphology was observed by an atomic force microscope (AFM), revealing the pressure dependence of nanostructures. The crystallographic structures of prepared TiO thin films were observed by X-ray diffraction (XRD). The optically observed band-gaps of the prepared thin films show that the crystallographic structures are mixed crystals of rutile and anatase. Evaporated Ti particles combine with buffer O
thin films were observed by X-ray diffraction (XRD). The optically observed band-gaps of the prepared thin films show that the crystallographic structures are mixed crystals of rutile and anatase. Evaporated Ti particles combine with buffer O gas thereby producing TiO molecules, which affect the formation of nanostructures on TiO
gas thereby producing TiO molecules, which affect the formation of nanostructures on TiO thin films.
thin films.
Iguchi, Tetsuo*; Watanabe, Kenichi*; Kawarabayashi, Jun*; Uritani, Akira*; Enokida, Yoichi*; Watanabe, Kazuo
JAERI-Tech 2004-010, 62 Pages, 2004/03
no abstracts in English